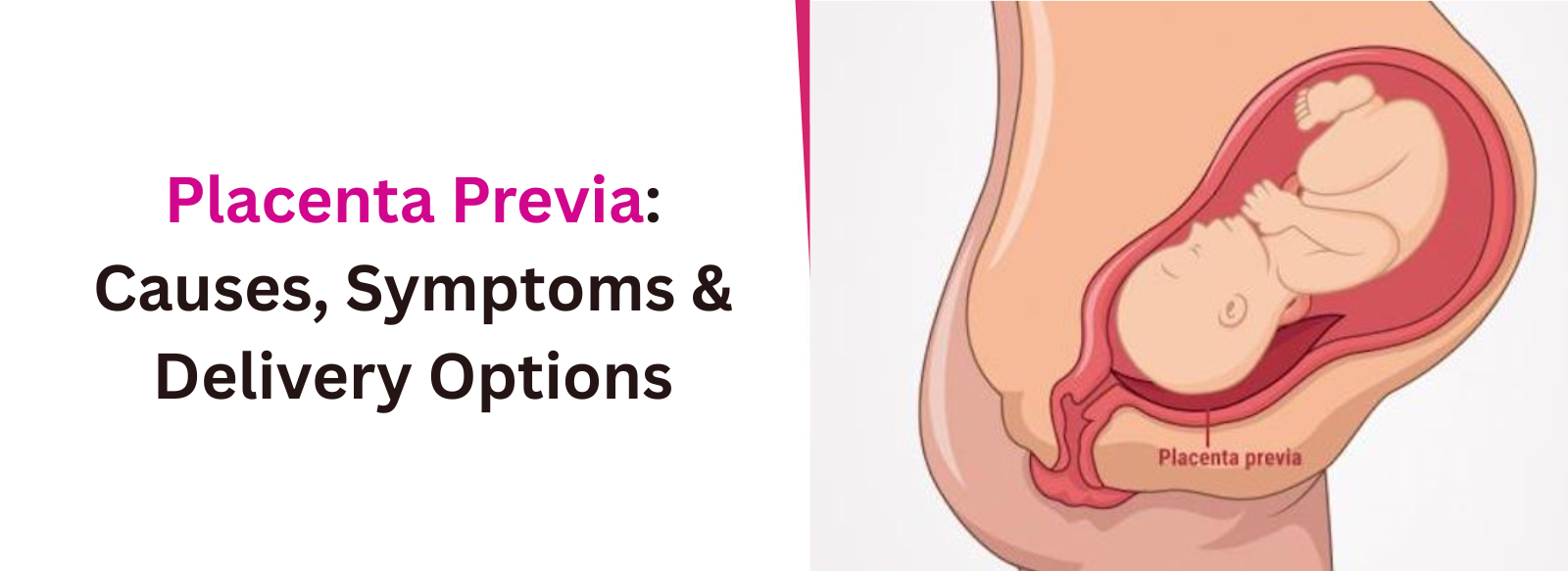
What is Placenta Previa? Placenta previa is a pregnancy condition where the placenta grows too low in the uterus and covers part or all of the cervix, the opening to the birth canal. This can cause complications during pregnancy and delivery, making early diagnosis and proper care very important. Placenta previa is not very common, affecting about 1 in every 200–500 pregnancies. However, women who conceive through IVF may face a slightly higher risk. At Vardaan IVF, we believe awareness is the first step toward safe motherhood. Knowing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for placenta previa helps expectant mothers prepare better for a healthy delivery.
Types & Classification of Placenta Previa
Doctors classify placenta previa based on how much of the cervix (the opening of the womb) is covered by the placenta. This classification is important because it directly affects pregnancy care and the delivery plan.- Marginal (Low-lying) – the placenta lies near the cervix but does not cover it.
- Partial – the placenta covers a portion of the cervix.
- Complete (Total) – the placenta completely covers the cervix.
Placenta Previa: Causes & Risk Factors
The exact cause of placenta previa is not fully known, but it is often linked to changes in the uterus, including scarring or damage from earlier procedures. These are some risks you should be aware of:- Previous C-section or uterine surgery (D&C, myomectomy)
- Advanced maternal age (35+)
- Multiparity, multiple pregnancy, prior placenta previa
- Smoking, cocaine use
- Assisted reproduction (e.g., IVF)
Placenta Previa: Symptoms & When to Seek Help
Placenta previa often shows its first signs in the second half of pregnancy. The most common symptom of placenta previa is painless, bright red vaginal bleeding that usually appears after 20 weeks of gestation.- Vaginal bleeding after 20 weeks (painless, bright red)
- Bleeding may start after intercourse or a medical exam
- Mild abdominal cramping or contractions
Placenta Previa: Diagnosis & Monitoring
Placenta previa is usually detected during routine ultrasound, often around the 20th week of pregnancy. Early screening helps identify the condition before serious symptoms appear.- Routine ultrasound at mid-pregnancy (around 20 weeks).
- Transvaginal ultrasound for more accurate results.
- Repeat scans to track placental movement.
Placenta Previa: Management Strategies
The treatment of placenta previa depends on how far along the pregnancy is, the severity of bleeding, and the mother’s overall health. Care is usually divided into two approaches.Expectant Management (if under 36 weeks and stable)
Activity modification: bed rest, avoid intercourse, heavy lifting, long standing, and pelvic exams.Hospital or outpatient monitoring depending on stability and bleeding episodes.Corticosteroids may be given to help the baby’s lungs mature if there is a risk of preterm delivery.Intervention When Indicated
Emergency or scheduled C-section based on gestational age and bleeding severity.=Blood transfusions if heavy bleeding occurs.In cases with placenta accreta spectrum (placenta grows too deeply into the uterus), doctors may plan a hysterectomy (surgical removal of the uterus) to control life-threatening bleedingPlacenta Previa: Delivery Options
For most women with placenta previa, a cesarean delivery is the safest choice. The timing and type of delivery depend on how much the placenta covers the cervix and whether bleeding occurs.- Elective C-section – usually planned around 36–37 weeks if the mother and baby are stable.
- Emergency C-section – required at any stage of pregnancy if severe bleeding starts.
- Vaginal delivery (rare) – may be considered only in minor or low-lying placenta previa under strict monitoring by an experienced medical team.
Placenta Previa: Complications & Prognosis
Placenta previa can create serious challenges for the mother. The main concern is heavy bleeding during pregnancy or delivery, which may sometimes require advanced medical care.- Heavy bleeding
- Hemorrhagic shock
- Anemia
- Hysterectomy
- ICU admission
- Rarely, maternal death
- Preterm birth
- Low birth weight
- Respiratory distress
- Growth restriction
- Stillbirth
Placenta Previa: Prevention & Lifestyle Recommendations
Placenta previa cannot always be prevented, but certain lifestyle choices and medical care can lower the risks. Staying cautious is especially important for women with high-risk pregnancies, including those conceived through IVF.- Avoid smoking and recreational drug use.
- Regular prenatal checkups for early detection.
- Timely ultrasound screening, especially in high-risk or IVF pregnancies.
Relevance to IVF Patients & Vardaan IVF’s Approach
Women who conceive through IVF have a slightly higher chance of developing placenta previa, which makes regular monitoring even more important. Awareness and timely medical care ensure safer outcomes for both mother and baby.- Proactive prenatal monitoring with advanced ultrasound scans.
- Personalized risk assessment for every IVF patient.
- Expert obstetric care to handle complications with confidence.